While CBD and THC are two of the most abundant hemp-derived cannabinoids, they are vastly different compounds. THC offers psychoactive, intoxicating effects, while CBD promotes a long list of wellness-boosting benefits.
Within the last few years, exciting interest in hemp plants has led to a vibrant, budding CBD market—a market that jumped to $1.9 billion in 2022.[1] Now, many adults rely on a vast variety of hemp-based CBD products and THC products for a number of therapeutic and recreational benefits.
The difference between the two cannabinoids may not be obvious, especially for beginners. And with all the information swirling around the web, finding a coherent answer can feel impossible to cannabis out. Here, we’ll do a deep dive into the origins of these cannabinoids, unpack their differences, and show you how to best enjoy them.
Cannabis 101: Hemp vs. Marijuana
The cannabis plant has quite an iconic shape: a five-fingered leaf with perforated edges and a skinny stem. It’s a simple design that’s donned on everything from T-shirts to stickers to billboards. But the term “cannabis” can apply to low-THC hemp and high-THC marijuana. The products on this site are made from legal hemp.
Both CBD and THC are compounds found in the cannabis plant, including hemp and marijuana. But, they don’t create the same experience. THC offers psychoactive, intoxicating effects, while CBD promotes a long list of non-psychoactive, wellness-boosting benefits.
What Is CBD?
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a chemical compound found in the cannabis hemp plant. It is one of over a hundred cannabinoids, which are compounds unique to the cannabis plant. Unlike the other most well-known cannabinoid, THC (or tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD is not psychoactive and does not produce a “high” sensation. Instead, CBD is known for its potential wellness benefits, as it interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the body, influencing various physiological processes to promote balance and well-being.
Will CBD Get You “High”?
CBD (cannabidiol) does not produce a “high” or intoxicating effect. Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychoactive and consuming CBD products should not result in the euphoric sensation commonly associated with marijuana use. However, many people get confused, since both THC and CBD are derived from the same plant, but CBD can be isolated from the THC compound found in the cannabis plant.[2]
Types of CBD
Whether considering full spectrum, broad spectrum, or CBD isolate, each CBD type brings its distinct characteristics to the forefront. This section delves into the nuances of these CBD varieties, offering insights into their individual properties, applications, and potential benefits.
Full Spectrum CBD
Full spectrum CBD is a form of CBD extract that contains the full array of cannabinoids, not limited to CBD alone. Extracted from the cannabis plant, full spectrum CBD retains trace amounts of THC, alongside other beneficial compounds, such as terpenes and flavonoids.[3] While the THC content in full spectrum CBD is below 0.3% by dry weight, its presence contributes to what is known as the Entourage Effect, where the combination of cannabinoids and compounds enhances the wellness potential of the CBD product.
Broad Spectrum CBD
Broad spectrum CBD refers to the type of CBD extract that encompasses a diverse spectrum of cannabinoids and other beneficial compounds found in the cannabis plant: similar to full spectrum CBD, but with detectable traces of THC filtered out. Broad spectrum retains the potential benefits of the Entourage Effect, where the interaction of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids synergistically enhances wellness benefits. Broad spectrum CBD is a suitable option for users seeking the benefits of a multitude of cannabis compounds without the (detectable) presence of THC.[4]
CBD Isolate
CBD isolate is a pure and crystalline form of CBD that has undergone a refining process to isolate and remove all other cannabinoids, terpenes, and plant materials from the cannabis extract. This results in a product that is 99% pure CBD, with no trace of THC or other cannabinoids. CBD isolate is often preferred by individuals who want to experience the potential benefits of CBD without any accompanying compounds.
What Is THC?
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant. It is responsible for the intoxicating effects commonly associated with marijuana use. When THC interacts with receptors in the brain and central nervous system, it produces the euphoric sensation of being “high.” While THC is found in varying concentrations in different cannabis strains, its concentration level is what distinguishes marijuana from hemp.
Will THC Get You “High”?
THC is the psychoactive compound in cannabis responsible for producing the characteristic “high” or euphoric effects. When THC interacts with the brain’s cannabinoid receptors, it induces alterations in perception, mood, and consciousness, leading to the elevated sensation.[5] The intensity of those effects can vary depending on factors, such as the method of consumption, dosage, individual tolerance, and the strain of cannabis.
Types of THC
THC stands as a central player in the cannabis industry, responsible for the psychoactive effects that many associate with cannabis consumption that keeps people coming back to the compound. Understanding the different types of THC can provide insights into the varying effects and potential associated with this prominent cannabinoid.
Delta 9 THC
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, commonly known as delta 9 THC, is the primary psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant. It’s responsible for the intoxicating effects that people often associate with marijuana use. Delta 9 THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the body, specifically binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system, leading to the characteristic euphoria or “high” experienced by users.
Delta 8 THC
Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol, commonly known as delta 8 THC, is another cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. It is structurally similar to the more well-known delta 9 THC, which is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis. Delta 8 THC, while also possessing psychoactive properties, is reported to produce a milder and more clear-headed buzz compared to delta 9 THC.
Delta 10 THC
Like delta 8 and delta 9, delta 10 THC is a psychoactive compound, but its effects are not as concentrated. Users of delta 10 claim that the use of the compound achieves a mellowed out, but energizing effect.[6]
THC-P
THC-P is a synthetic cannabinoid that belongs to the family of trace compounds found in cannabis. It is structurally similar to the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, THC. THC-P interacts with the CB1 and CB2 receptors of the body’s endocannabinoid system, producing elevated effects estimated at 30-times-greater than that of D9 THC.[7]
HHC
HHC, or hexahydrocannabinol, is a synthetic cannabinoid that shares structural similarities with THC.[8] Like THC-P, HHC interacts with the CB1 and CB2 receptors of the endocannabinoid system. HHC is created through chemical synthesis. Some individuals use synthetic cannabinoids for recreational purposes, seeking experiences similar to those produced by cannabis. However, it has been reported that HHC produces a much more mild level of elevation.
Similarities & Differences Between CBD and THC
While CBD and THC share some similarities, they also have distinct differences, particularly in their effects on the body and mind. Both CBD and THC are derived from the cannabis plant and have a similar chemical structure, both containing 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms.[9]
Both cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system in the human body, influencing many processes from mood to appetite. However, while THC is psychoactive and responsible for the “high” or euphoric feeling associated with marijuana use, CBD is non-psychoactive and does not produce a high feeling.
Both CBD and THC have potential wellness benefits, but their applications differ. CBD is commonly used to alleviate stress and light pain, as THC is utilized recreationally or can even be prescribed for specific medical conditions.
THC may cause side effects, such as increased heart rate, dry mouth, and impaired coordination. CBD, in general, is considered well-tolerated with few side effects, though individual responses may vary.
THC consumption can lead to positive drug test results, as many drug tests are designed to detect THC metabolites. CBD products with low or no THC content are less likely to trigger positive drug tests.
It’s important to note that the effects of cannabinoids can vary depending on factors such as dosage, individual sensitivity, and the presence of other compounds in the cannabis plant. Additionally, ongoing research continues to uncover more about the therapeutic potential and safety of both CBD and THC.
CBD Products vs. THC Products
When it comes to cannabis-derived products, the dynamic interplay between CBD and THC stands at the forefront of discussions. While both compounds originate from the cannabis plant, they diverge significantly in their effects and applications. This section explores the distinctions between CBD and THC products, shedding light on their unique properties, potential benefits, and potential drawbacks.
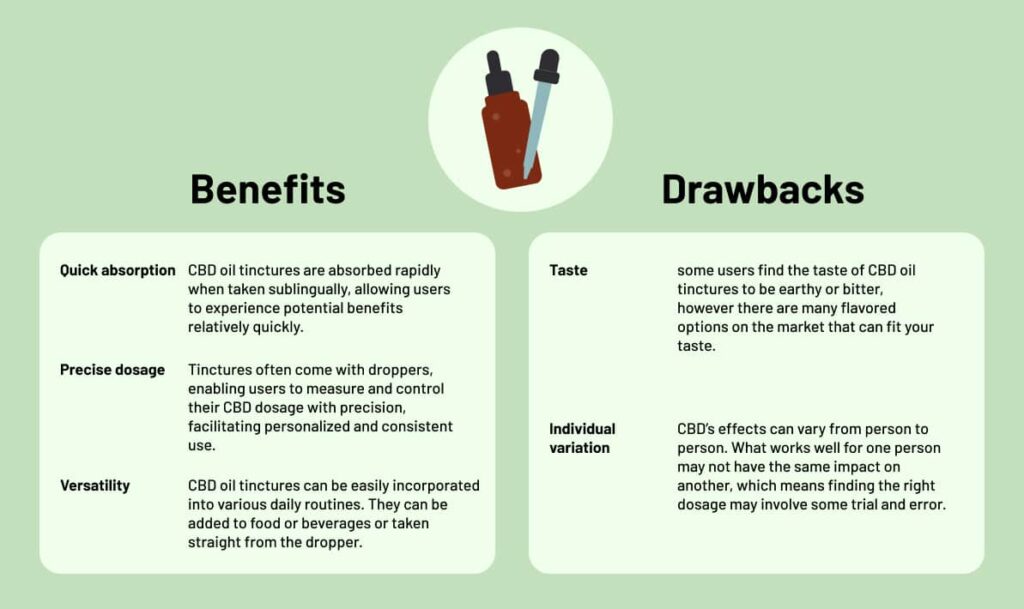
Oil Tinctures
Oil tinctures are liquid extracts containing CBD or THC. Typically, these tinctures involve infusing CBD or THC with a carrier oil, such as hemp seed oil or MCT oil, to enhance absorption. Users can administer oil tinctures sublingually (under the tongue) for quick absorption into the bloodstream, making them a popular and convenient method for experiencing the potential therapeutic effects of CBD and elevated nature of THC.
Edibles
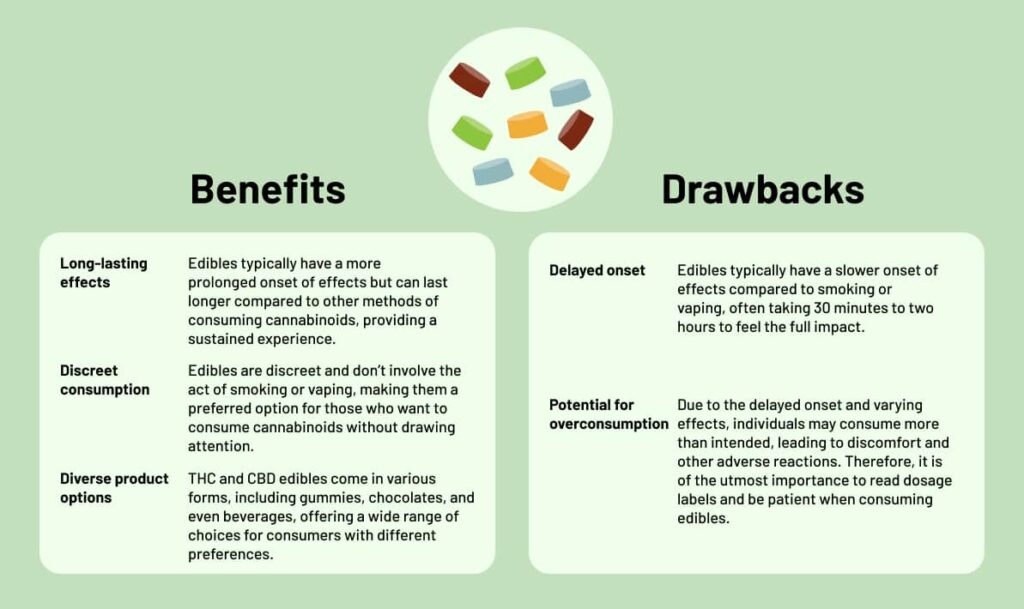
Edibles are cannabis-infused ingestible products or beverages containing cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD. These products offer an alternative method of consuming cannabis compared to smoking or vaping. Edibles come in various forms, including gummies, beverages, and more.

When consumed, the cannabinoids in edibles are metabolized by the liver, leading to a slower onset of effects compared to smoking, vaping, or sublingual oils. The effects can take anywhere from 30 minutes to two hours to manifest fully, but they tend to last longer. Edibles like CBDfx Mixed Berry CBD Gummies or Delta 8 THC Gummies from TRĒ House are known for providing a discreet way to consume cannabis or CBD without the need for smoking, making them a popular choice for individuals who prefer a more inconspicuous method.

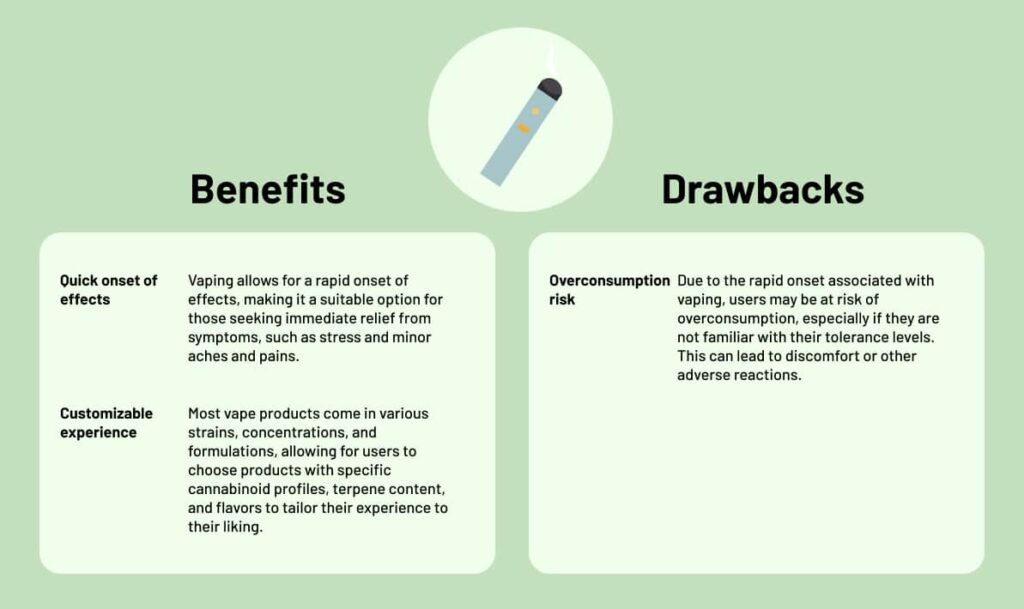
Vapes
Vapes, short for vaporizers, are devices designed to heat substances, such as CBD or THC, to a temperature that produces vapor rather than smoke. CBD and THC vapes are designed to heat infused concentrates like oils or resin to a temperature that releases cannabinoids and terpenes in the form of vapor. Cannabis vaporizers come in various flavors, like the Blue Raspberry CBD Vape Pen from CBDfx and Binoid’s Live Resin THC Vape Pen, and forms including disposable pens or refillable cartridges.


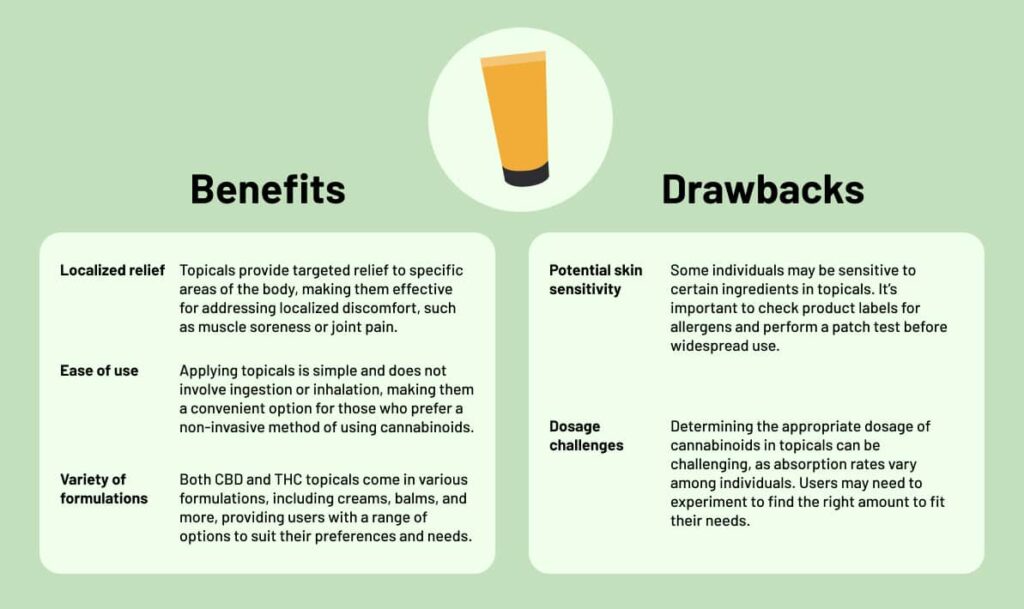
Topicals
CBD and THC topicals are products infused with the cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol cannabinoids, which are compounds found in the cannabis plant. These topicals are designed for external use on the skin and are formulated to provide localized relief without the psychoactive effects associated with consuming cannabis.
CBD-infused creams and lotions are common topicals designed to be applied directly to the skin. They are often used for skin care or to address localized discomfort. CBD balms and salves are thicker formulations that may contain additional ingredients, such as beeswax or shea butter, and are intended for targeted application on specific areas of the body. Similar to CBD balms, THC-infused balms and salves are designed for localized relief. They are applied directly to the skin and may contain other soothing ingredients.
Which Cannabinoid Is Right for You?
Finding the right cannabinoid for your needs involves a thoughtful and individualized approach. Start by identifying your specific wellness goals, whether it’s relief from minor aches and pains, stress, or other issues. Experiment with different cannabinoids, like CBD or THC, in various forms, like oil tinctures, edibles, or topicals, to determine which suits you best. Pay attention to dosage, starting with lower amounts and gradually adjust your dosage accordingly.
Choose products from reputable sources that provide clear information about their contents and undergo third-party testing for quality and purity. Keeping a journal to track your experiences can be helpful in refining your preferences and finding the cannabinoid product that aligns with your unique needs and lifestyle.
Final Thoughts
Cannabinoids, particularly CBD and THC, are vast and complex, offering a spectrum of therapeutic and recreational possibilities. The distinction between these compounds lies not only in their chemical structures, but also in their effects on the body and mind. CBD, known for its non-psychoactive nature, provides a myriad of potential wellness benefits, while THC, with its psychoactive properties, is associated with the euphoric “high” commonly linked to marijuana use. From oil tinctures to edibles, vapes, and topicals, the diverse array of products reflects the dynamic interplay between CBD and THC in the evolving landscape of cannabis consumption. As users seek the right cannabinoid for their individual needs, a thoughtful and personalized approach, coupled with attention to dosage and product quality, becomes paramount in unlocking the full potential of these compounds for enhanced well-being.
—-
- Hall, A. (2023, June 22). CBD Statistics, Data And Use (2024). Forbes Health. https://www.forbes.com/health/cbd/cbd-statistics/#cbd_statistics_at_a_glance_section
- Holland, Kimberly. “Can You Get High from CBD or CBD Oil?” Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/does-cbd-get-you-high. 23 August 2019.
- Jesner, Leoni. “Full-Spectrum CBD: What It Is, Benefits And Risks” Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/health/cbd/full-spectrum-cbd/. Updated 8 November 2023.
- Mona, Breanna. “What Is Broad-Spectrum CBD?” Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/broad-spectrum-cbd. Updated 31 August 2023.
- NIDA. “How does marijuana produce its effects?.” National Institute on Drug Abuse, 13 Apr. 2021, https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/how-does-marijuana-produce-its-effects Accessed 15 Jan. 2024.
- Ferguson, Sian. “Delta 8 vs. Delta 9 vs. Delta 10 — What’s the Difference?” Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/delta-8-vs-delta-9-vs-delta-10#delta-10-effects. 28 September 2022.
- Green, Mell. “All You Need to Know About THCP” CBD Oracle, https://cbdoracle.com/cannabinoids/thcp/. 6 June 2023.
- Frysh, Paul. “HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol): Uses, Side Effects, and More” WebMD, https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/addiction/what-is-hhc. 6 December 2023.
- Fletcher, Jenna. “A comparison of CBD and THC” Medical News Today, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325871. Updated on 19 October 2023.



